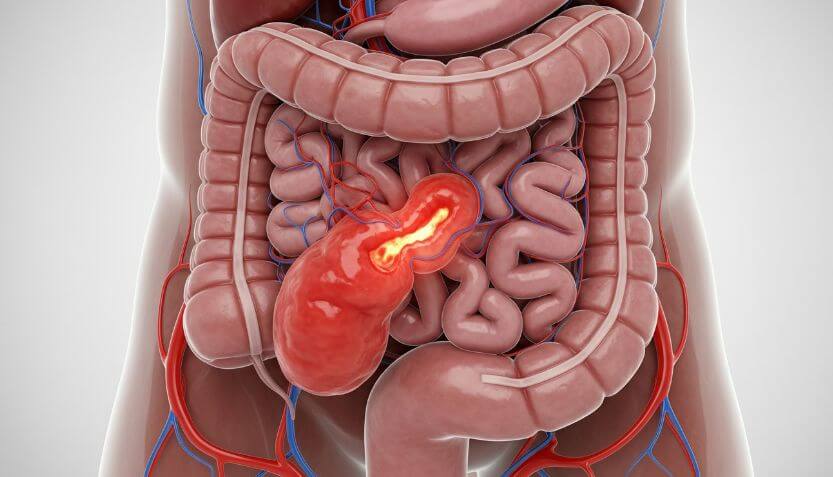
Appendicitis is one of the most common surgical emergencies, yet many people delay seeking treatment because they mistake its early signs for common stomach problems. The appendix is a small, finger-shaped pouch attached to the large intestine. When it becomes inflamed or infected, it causes appendicitis. If not treated in time, it may burst and lead to life-threatening complications.
Recognizing the early symptoms of appendicitis is crucial because timely medical help can save a patient from severe health risks. This blog explains the early warning signs, causes, risk factors, and when you should see a doctor.
What is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes blocked, usually by stool, infection, or swelling. This blockage causes bacteria to multiply, leading to inflammation, pain, and sometimes pus formation.
If left untreated, the appendix can rupture, spreading infection throughout the abdomen (peritonitis), which can be life-threatening. This is why recognizing symptoms early and seeking prompt treatment is very important.
Why is Early Detection Important?
- Prevents complications like rupture and severe infection.
- Allows treatment with a simple surgery called appendectomy, usually done laparoscopically.
- Reduces recovery time and hospital stay.
- Ensures patients return to normal life quickly.
Early Symptoms of Appendicitis
1. Abdominal Pain
- The most common and early symptom of appendicitis.
- Pain usually starts around the belly button and then shifts to the lower right side of the abdomen.
- The pain may worsen when coughing, walking, or making sudden movements.
2. Loss of Appetite
- Patients may suddenly lose interest in eating.
- This loss of appetite often appears before nausea or vomiting begins.
3. Nausea and Vomiting
- Shortly after the abdominal pain starts, nausea or vomiting may follow.
- These symptoms should not be ignored if they occur together with lower right abdominal pain.
4. Low-Grade Fever
- A mild fever between 99°F (37.2°C) and 100.5°F (38°C) may develop.
- As the infection worsens, the fever may rise.
5. Digestive Disturbances
- Constipation, diarrhea, or difficulty passing gas may occur.
- The abdomen may feel bloated or swollen.
6. Abdominal Tenderness
- When gentle pressure is applied to the lower right abdomen, tenderness and pain are felt.
- This is a key sign doctors check during physical examination.
Other Symptoms That May Occur
- Pain that worsens with movement, coughing, or sneezing.
- A general feeling of being unwell and fatigued.
- Swelling of the abdomen in severe cases.
When to See a Doctor Immediately
You should seek urgent medical attention if you or a loved one experiences the following:
- Sudden pain that begins near the belly button and shifts to the lower right abdomen.
- Pain that intensifies within a few hours.
- Nausea and vomiting with abdominal pain.
- Loss of appetite and low-grade fever together.
- Difficulty standing straight or walking because of abdominal pain.
⚠️ Do not take painkillers or apply heat to the abdomen before consulting a doctor, as this can mask symptoms and worsen the condition.
Who is at Risk of Appendicitis?
- People between 10–30 years of age (though it can occur at any age)
- Individuals with frequent gastrointestinal infections.
Diagnosis of Appendicitis
Doctors use a combination of:
- Physical examination – Checking tenderness in the lower right abdomen.
- Blood tests – To detect infection.
- Ultrasound or CT scan – To confirm inflammation of the appendix.
Treatment Options for Appendicitis
1. Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- Minimally invasive surgery using small cuts.
- Faster recovery, less pain, and small scars.
- Most commonly preferred method today.
2. Open Appendectomy
- Done if the appendix has already ruptured or if laparoscopic surgery isn’t possible.
- A larger incision is made to remove the appendix and clean the infection.
3. Antibiotics
- Sometimes antibiotics are given before surgery to reduce infection.
- In rare cases, very mild appendicitis may be treated with antibiotics alone, but surgery remains the standard treatment.
Recovery After Appendicitis Surgery
- Most patients recover within 1–2 weeks after laparoscopic surgery.
- Normal diet is resumed gradually.
- Heavy physical activity should be avoided for a few weeks.
- Regular follow-ups ensure complete healing.
Prevention Tips
There is no guaranteed way to prevent appendicitis, but you can lower your risk by:
- Eating a diet rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grains).
- Drinking plenty of water daily.
- Avoiding junk food and processed items.
- Maintaining overall digestive health.
Conclusion
Appendicitis is a condition that should never be ignored. The early symptoms – abdominal pain, nausea, loss of appetite, low-grade fever, and digestive issues; must be taken seriously. Immediate medical attention and timely surgery can prevent life-threatening complications.
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, consult a qualified doctor without delay. With modern laparoscopic surgery, recovery is faster, safer, and more comfortable.
Related Posts
Common Gastrointestinal Problems & When to Se...
Digestive health plays a very important role in our daily life. When our gastrointestinal (GI) system is not working pro...
Read MoreHow Long Does GI Surgery Recovery Take?...
Gastrointestinal (GI) surgery is often recommended when digestive problems cannot be treated with medicines or lifestyle...
Read More