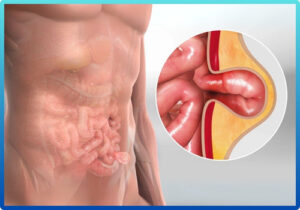
 Hernia surgery
Hernia surgery
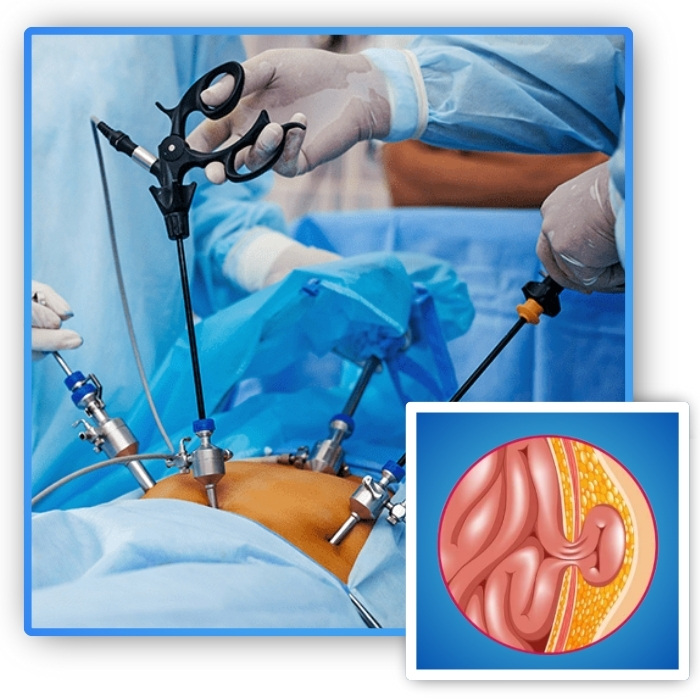
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue, often appearing as a visible bulge. Common types include inguinal, umbilical, and incisional hernias, typically affecting the abdomen or groin. Symptoms may include discomfort, pain during lifting or bending, and swelling that may worsen over time. If left untreated, a hernia can lead to serious complications such as strangulation, where blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off. Laparoscopic hernia surgery is a minimally invasive technique that uses small incisions and a camera to repair the weakened area with mesh reinforcement, offering reduced pain, quicker recovery, and minimal scarring. Early evaluation by one of the best hernia surgery doctors in Bhubaneswar, Dr. Lalatendu Mahapatra, along with timely surgical correction, is crucial to prevent complications and ensure long-term relief from hernia-related symptoms.
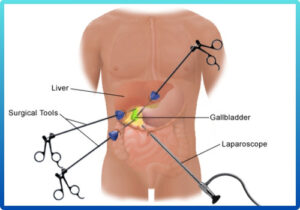 Gallbladder Surgery
Gallbladder Surgery
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver that stores and releases bile to help digest fats. When substances in the bile, such as cholesterol, form solid particles, they can develop into gallstones, leading to pain, nausea, indigestion, and sometimes infection. This condition, known as cholelithiasis, can cause severe discomfort, especially after meals. In many cases, the best treatment is a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, a minimally invasive surgery to remove the gallbladder. This procedure involves small incisions, minimal pain, quicker recovery, and less scarring compared to traditional open surgery. Laparoscopic removal of the gallbladder is safe and commonly performed when gallstones cause recurrent symptoms or complications such as inflammation or bile duct blockage. Timely surgical intervention can prevent further health issues and improve quality of life.
Appendix Surgery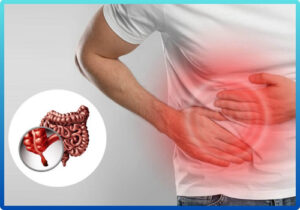
The appendix is a small, tube-like organ attached to the large intestine, located in the lower right side of the abdomen. While its exact function remains unclear, it can become inflamed due to infection or blockage, a condition known as appendicitis. This often causes sudden abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. If left untreated, an inflamed appendix can rupture, leading to serious complications like peritonitis. Laparoscopic appendectomy is a common and minimally invasive procedure used to remove the appendix safely and effectively. It involves small incisions, less pain, faster recovery, and minimal scarring compared to open surgery. Appendix surgeries performed using advanced laparoscopic techniques ensure precision and better outcomes. For such conditions, many patients prefer consulting Dr. Lalatendu Mahapatra – among the best appendix surgery doctors in Bhubaneswar – for accurate diagnosis and expert surgical care. Early diagnosis and timely surgical intervention are key to avoiding complications associated with appendicitis.
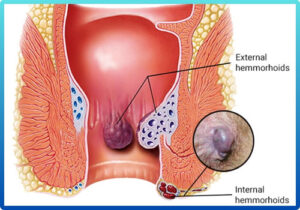 Piles Surgery
Piles Surgery
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus that can cause pain, bleeding, itching, and discomfort during bowel movements. When lifestyle changes and medications fail to provide relief, piles surgery becomes a safe and effective treatment option. Modern procedures like laser hemorrhoidectomy and stapler surgery offer minimal pain, faster healing, and quicker return to daily activities. These advanced techniques reduce bleeding, swelling, and post-operative discomfort, ensuring better long-term outcomes. For expert evaluation and advanced treatment, many patients trust Dr. Lalatendu Mahapatra, one of the best piles surgeons in Bhubaneswar, known for his precision and patient-focused care. Early consultation with an experienced specialist ensures timely relief and prevents complications.

 Hernia surgery
Hernia surgery Gallbladder Surgery
Gallbladder Surgery
 Piles Surgery
Piles Surgery